CD4+ T cell
Immune-Oncology Assays
- Polyclonal
- MLR
- Antigen specificity
- nTreg suppression assay
- iTreg polarisation assay
Autoimmunity Assays
- Th1/2/17 polarisation
- Th17 function
- Tr1/iTreg polarisation
- nTreg suppression
- Tfh, naïve
- CM and EM phenotype/function
- Polyclonal T cell proliferation
- Cytokine release
Inflammation Assays
- Cytokine release
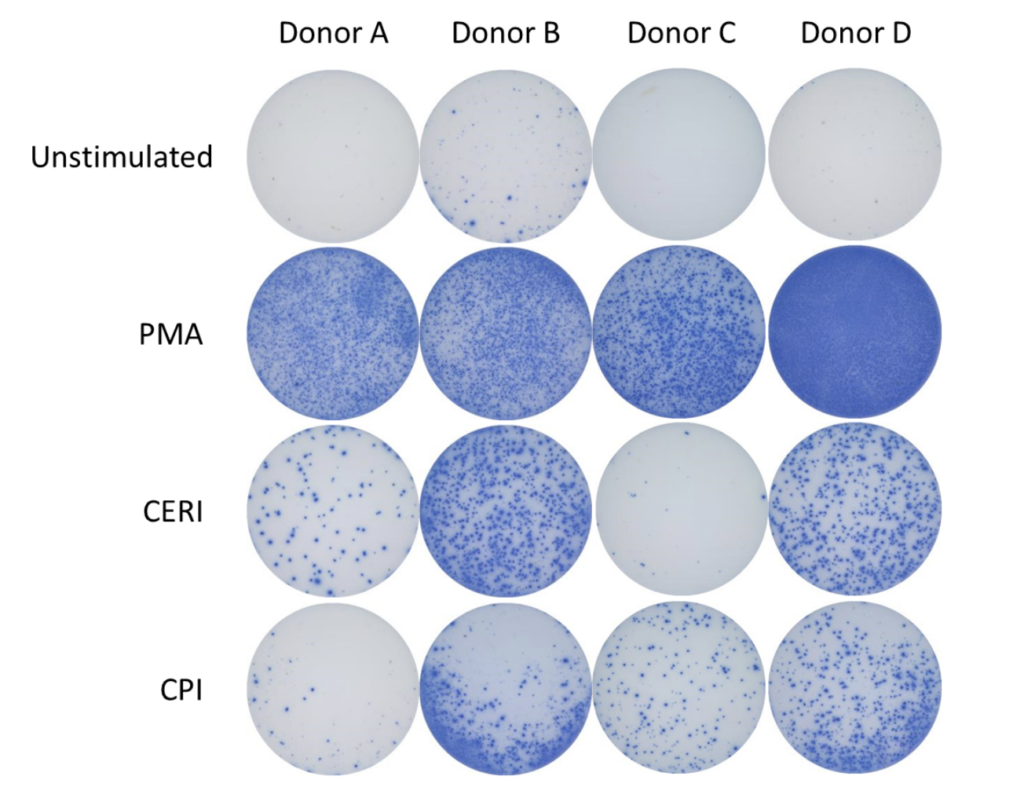
Enzyme-Linked Immuno Spot (ELISpot) is a technique which quantifies rare immune cells that release biomarkers such as cytokines in response to antigenic stimulation. ELISpot is a highly sensitive method to test immune modulators, novel vaccine candidates or de-risk immunogenicity testing in an antigen-specific CD4 and/or CD8 T cell assay.
| Condition | Aim |
| No Stimulation | Negative control |
| PMA | Positive control |
| CERI (CMV, EBV, RSV, Influenza) | MHC-I restricted peptide pool to evaluate modulation of CD8+ T-cell memory response |
| CPI (CMV, Parainfluenza, Influenza) | Positive protein antigens to evaluate modulation of CD4+ T-cell memory response |
| CEF (CMV, EBV, Influenza) | MHC-I restricted peptide pool to evaluate modulation of CD8+ T-cell memory response |
| Cyclosporin A (CsA) | Inhibition of immune response |
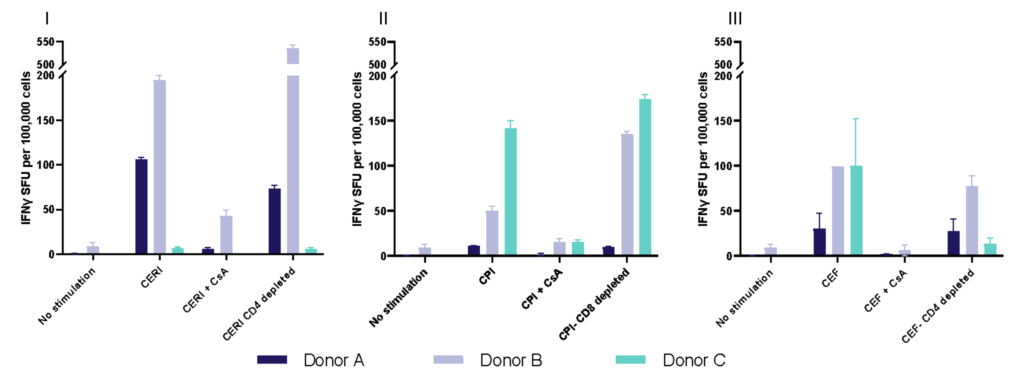
Spot Forming Units (SPU) for IFN-γ per 100,000 PBMC from CERI, CPI and CEF antigens for three donors
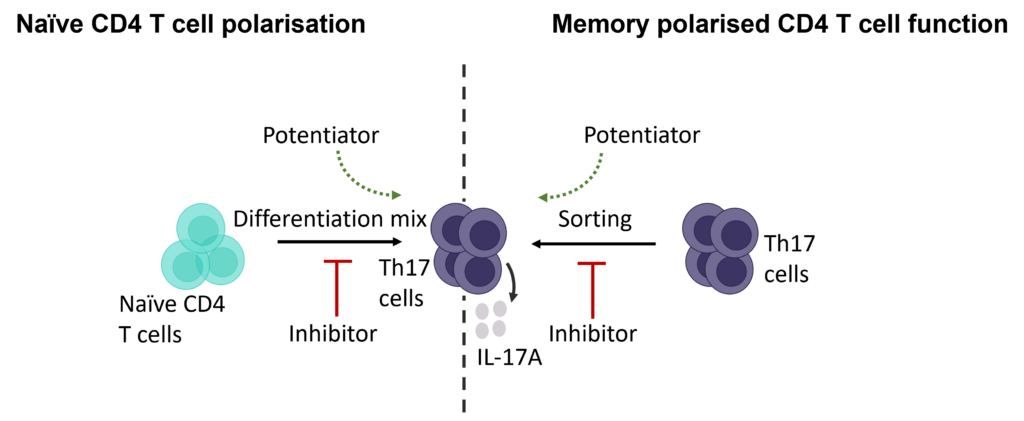
Therapeutic modulation of TH17 CD4+ T cell differentiation or effector function
T helper 17 (Th17) cells, are a subset of CD4 T cells distinguished by their production of IL-17. While crucial for protecting the body against extracellular pathogens, Th17 cells have also been implicated in autoimmune disease. Discovering therapies that target either the differentiation or effector function of Th17 cells could therefore prove beneficial for the treatment of some autoimmune diseases.
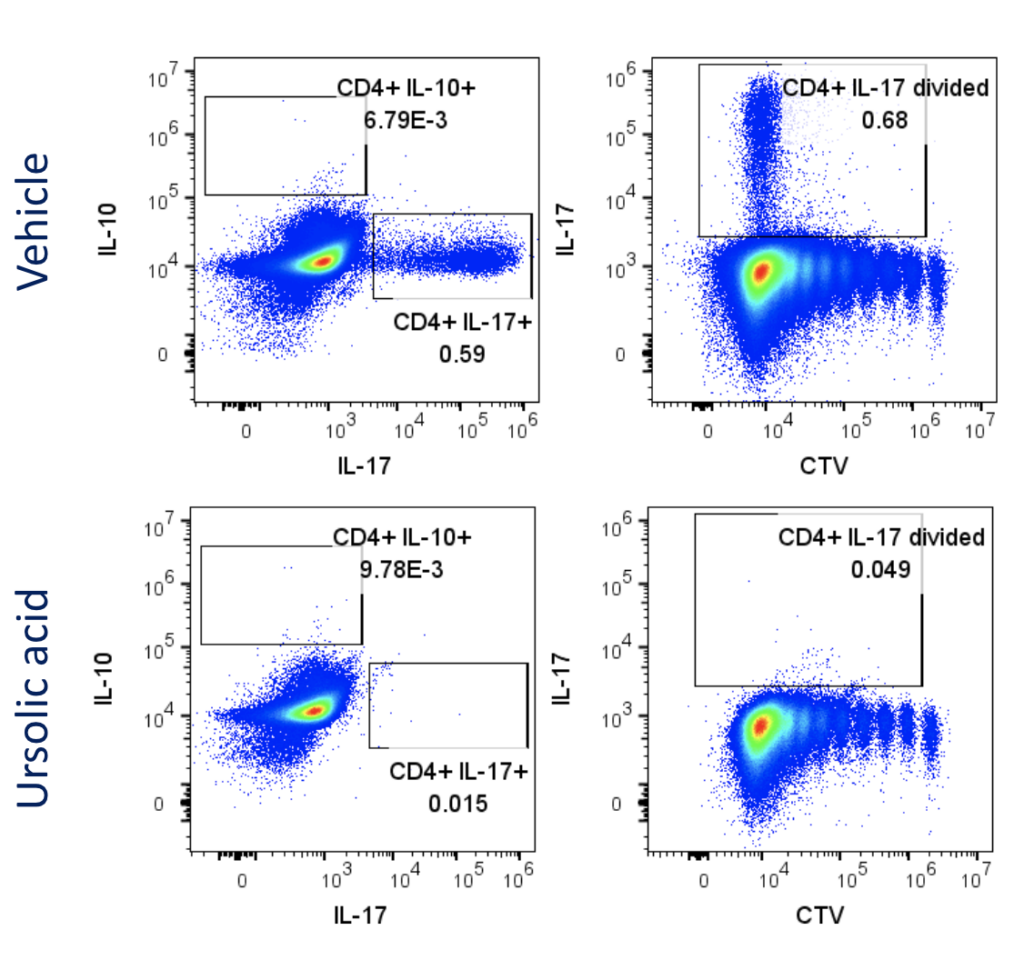
Evaluation of therapeutic modulation of Th17 differentiation
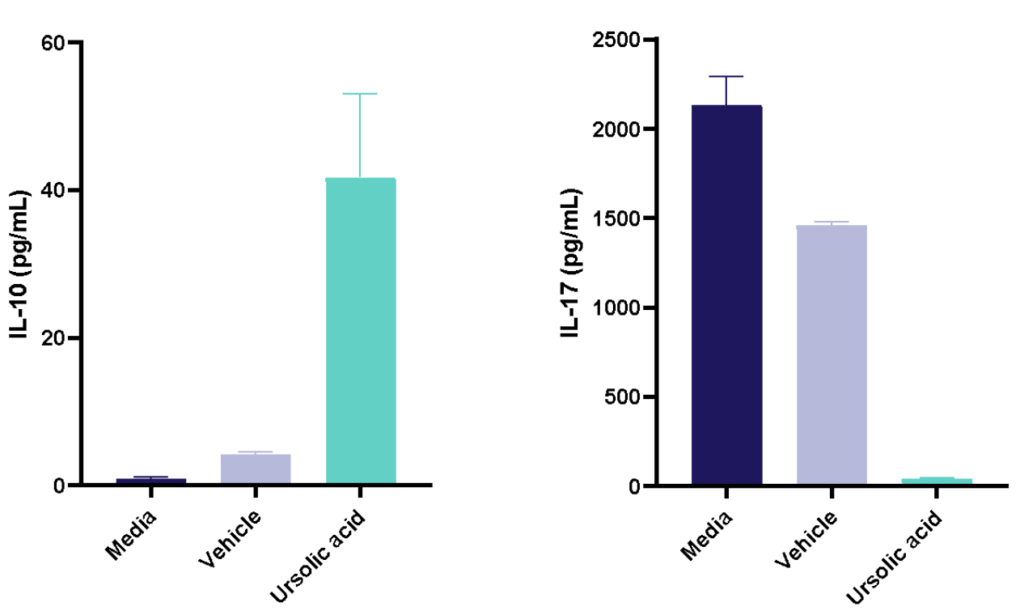
Figure 1: Polarisation of Th17 cells. Naïve CD4 cells were cultured under Th17 polarising conditions for 12 days in the presence or absence of Ursolic Acid. CD4 T cells were assessed for proliferation by CTV dilution; intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) of IL-17 and IL-10 by flow cytometry. On Day 12, Supernatants were collected and evaluated for IL-17 and IL-10 levels by MSD. RoRγT inhibitor Ursolic Acid showed selective inhibition of IL-17 production by intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) and MSD.
Evaluation of therapeutic modulation of Th17 effector function
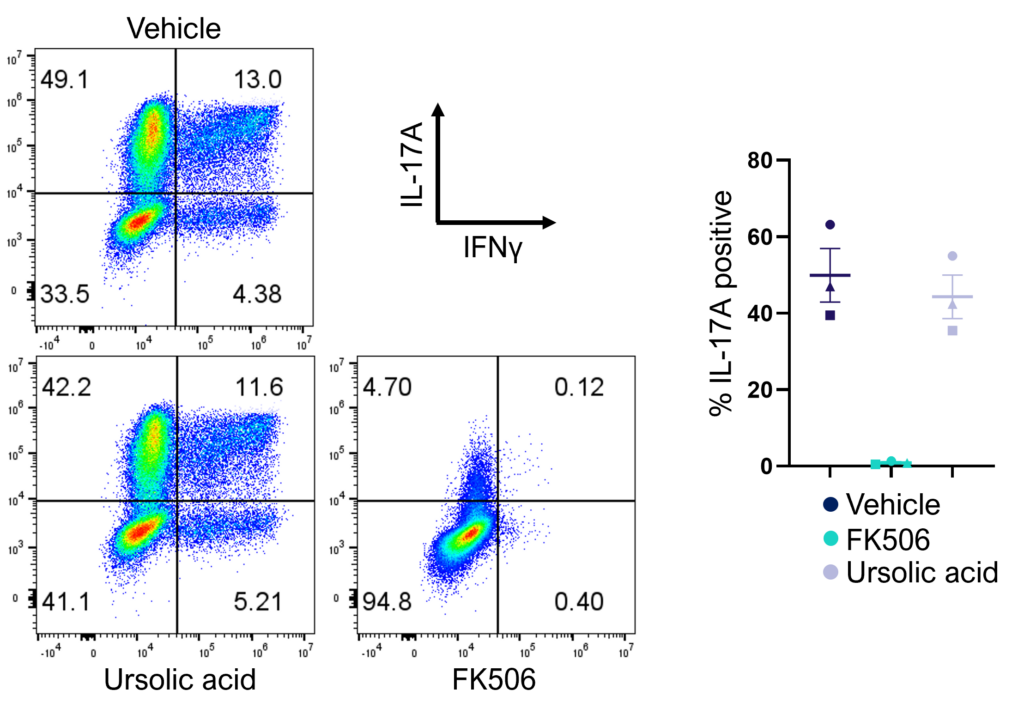
Figure 2: Inhibition of Th17 cell effector function. Magnetically sorted memory Th17 cells were polyclonally stimulated under Th17 conditions in the presence or absence of ursolic acid or FK506 for 5 days. A percentage of Th17 cells are polyfunctional (IL- 17A+IFNg+) and refractory to inhibition by ursolic acid (an inhibitor of Th17 differentiation) but not FK506.
Evaluation of therapeutic modulation of antigen-specific memory T cell responses to recall antigens
I. T cell response to Tetanus Toxoid, Influenza and PPD antigens
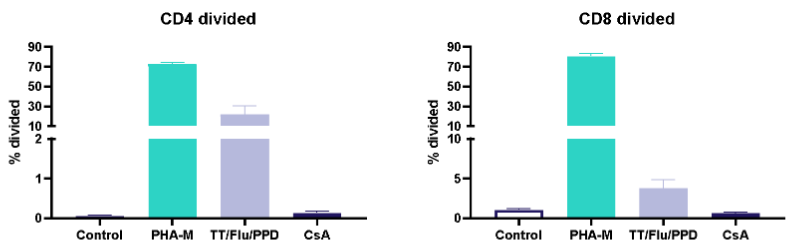
II. Dose response to Influenza antigen
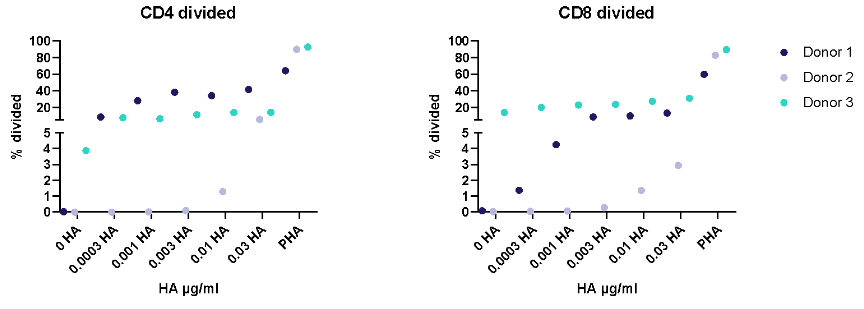
Antigen specific T cells response to a recall antigens. (I) Healthy donors PBMC were stimulated with PHA-M or triple antigen cocktail (Tetanus Toxoid, Influenza and PPD). Cyclosporin was used as a reference treatment. (II) Dose response to Influenza antigen. CD4 and CD8 T cells proliferation was measured by flow cytometry using CTV dilutions.
Enhance T cell effector function: benchmark novel therapies against immune checkpoint blocker (anti-PD-1) in a 1-way MLR

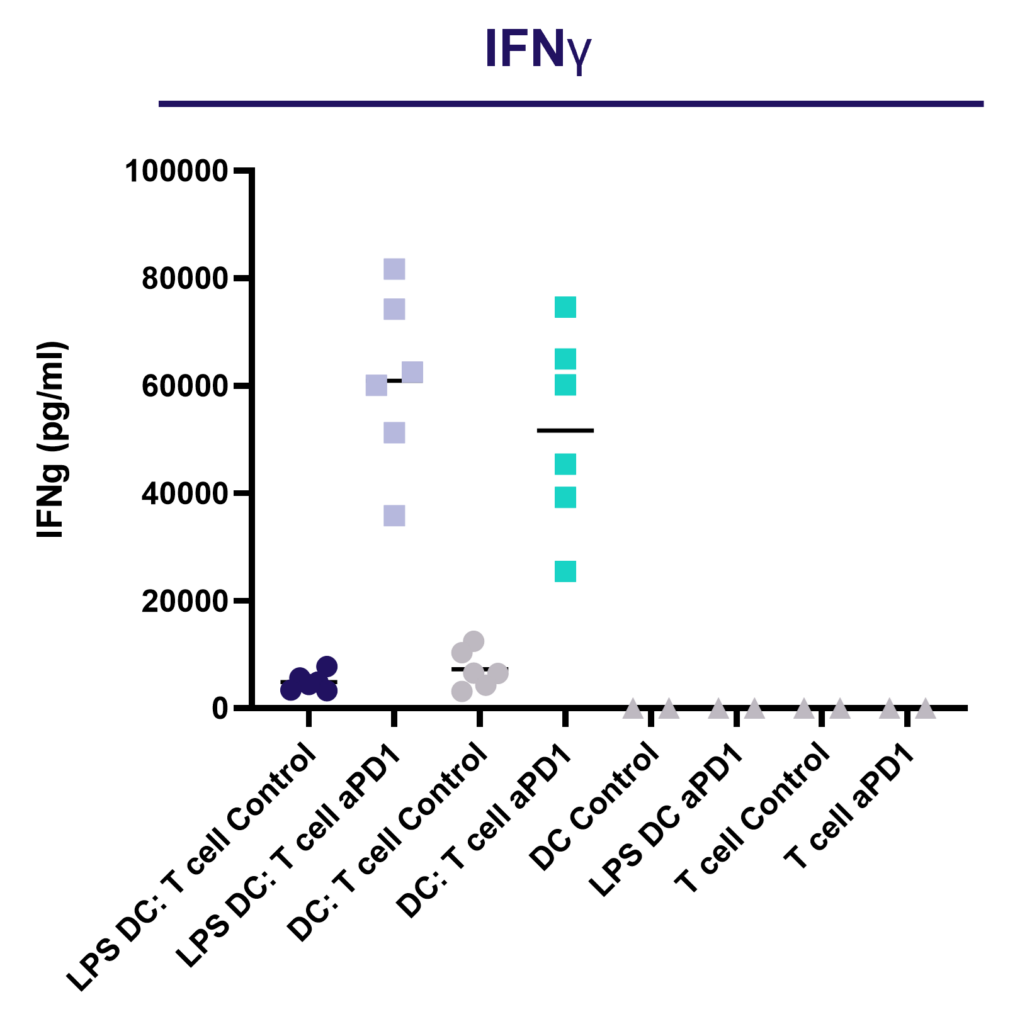
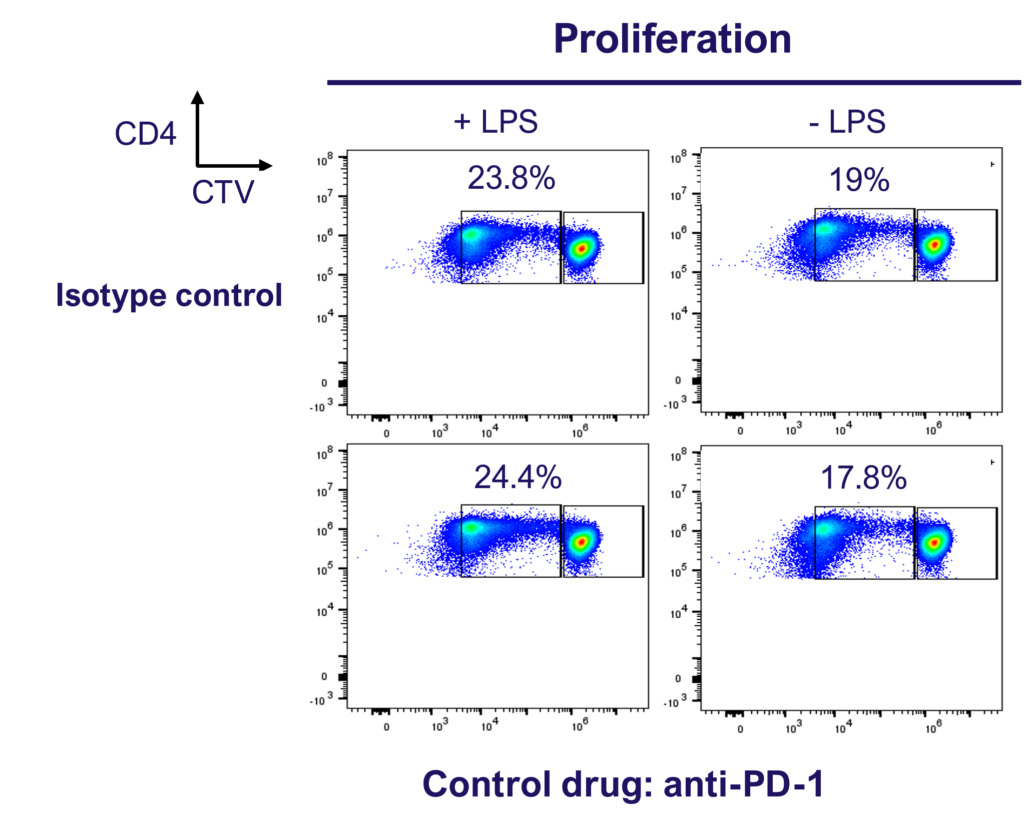
PD-1 blockade does not enhance CD4 T cell proliferation in a 1-way MLR as determined by dye dilution of CTV labelled CD4 T cell using flow cytometry.

Drug Discovery Tool
Find the right immune assay for your therapeutic area, modality and target using this interactive Drug Discovery Tool.
