Antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) in a 3D tumour spheroid model
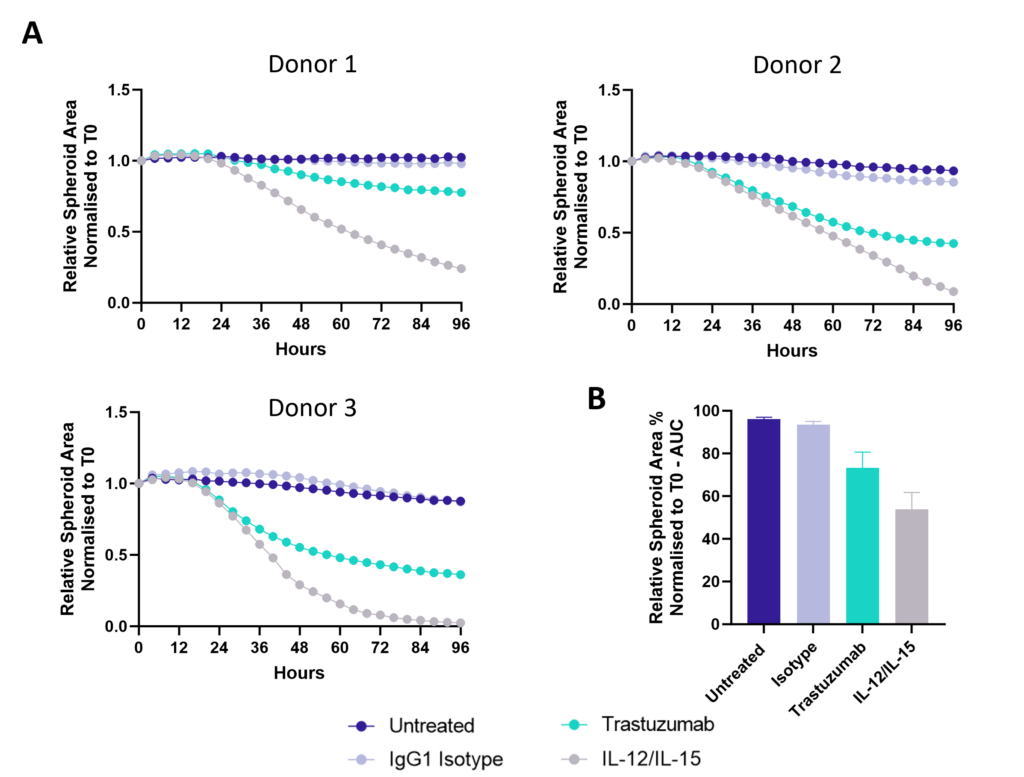
Figure 1: SK-OV-3 NLR cells expressing HER2 were plated were seeded into 96 well plates and once spheroids were established purified NK cells were added to cultures in the presence of Trastuzumab or IgG1 Isotype or IL-12/IL-15 or vehicle (untreated) and imaged every 4 hours for 96 hours using the CellCyte X. Relative spheroid area (%) was measured (A) and the AUC (B) calculated using GraphPad Prism v9.5.0. Line graphs show the mean of triplicate wells and the bar graph shows mean +/- SEM of 3 donors. (C) Representative images from the CellCyte X at 96 hours post NK cell addition to tumour spheroids.
Enzyme-Linked Immuno Spot (ELISpot) is a technique which quantifies rare immune cells that release biomarkers such as cytokines in response to antigenic stimulation. ELISpot is a highly sensitive method to test immune modulators, novel vaccine candidates or de-risk immunogenicity testing in an antigen-specific CD4 and/or CD8 T cell assay.
| Condition | Aim |
| No Stimulation | Negative control |
| PMA | Positive control |
| CERI (CMV, EBV, RSV, Influenza) | MHC-I restricted peptide pool to evaluate modulation of CD8+ T-cell memory response |
| CPI (CMV, Parainfluenza, Influenza) | Positive protein antigens to evaluate modulation of CD4+ T-cell memory response |
| CEF (CMV, EBV, Influenza) | MHC-I restricted peptide pool to evaluate modulation of CD8+ T-cell memory response |
| Cyclosporin A (CsA) | Inhibition of immune response |
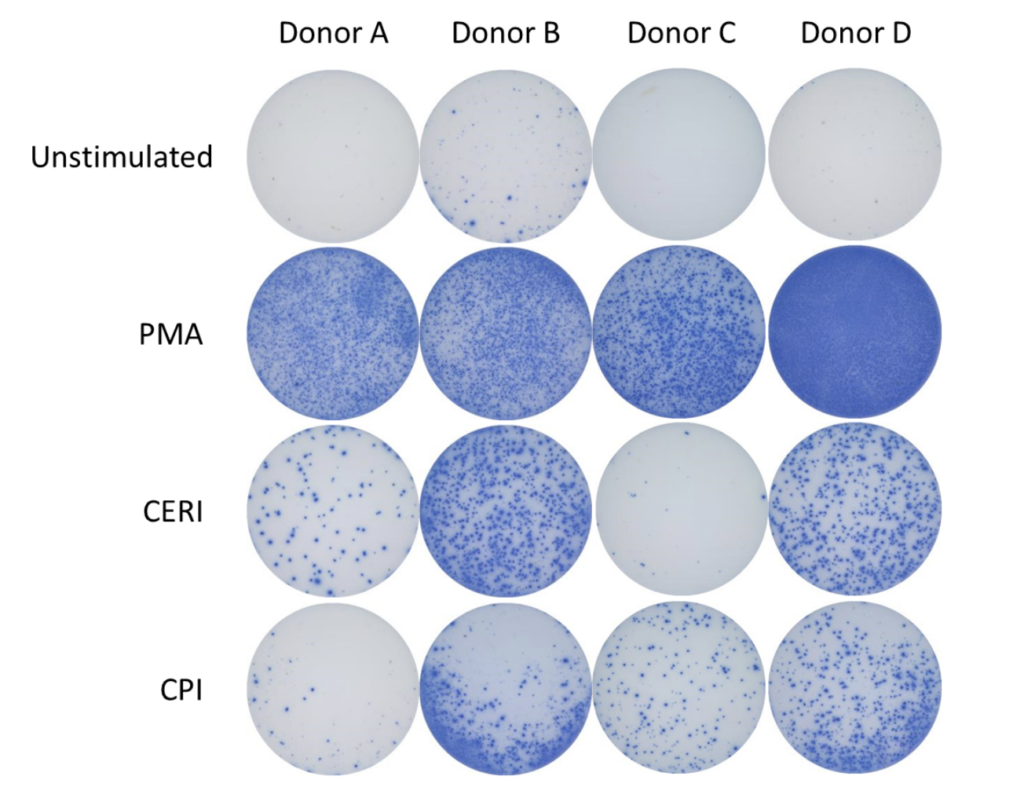
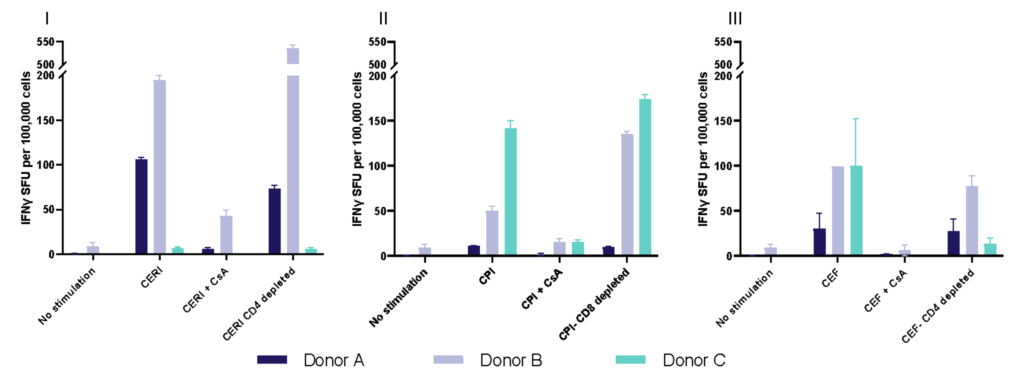
Spot Forming Units (SPU) for IFN-γ per 100,000 PBMC from CERI, CPI and CEF antigens for three donors
Therapeutic modulation of TH17 CD4+ T cell differentiation or effector function
T helper 17 (Th17) cells, are a subset of CD4 T cells distinguished by their production of IL-17. While crucial for protecting the body against extracellular pathogens, Th17 cells have also been implicated in autoimmune disease. Discovering therapies that target either the differentiation or effector function of Th17 cells could therefore prove beneficial for the treatment of some autoimmune diseases.
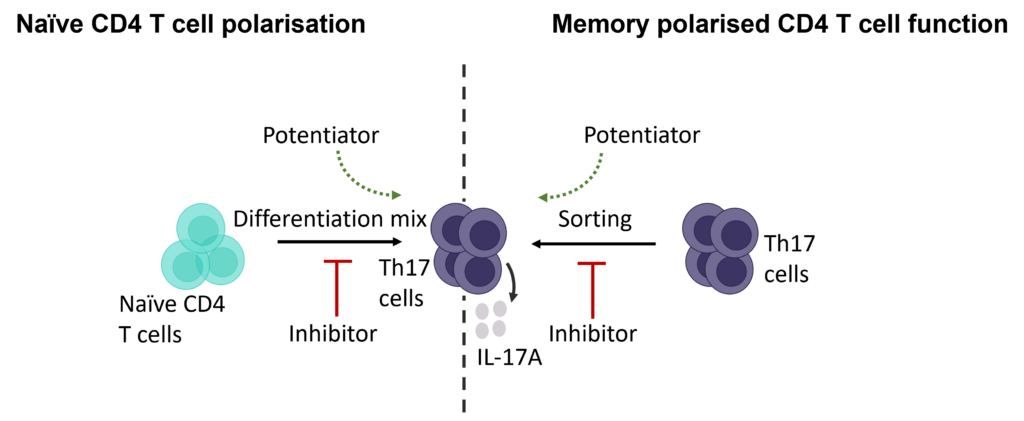
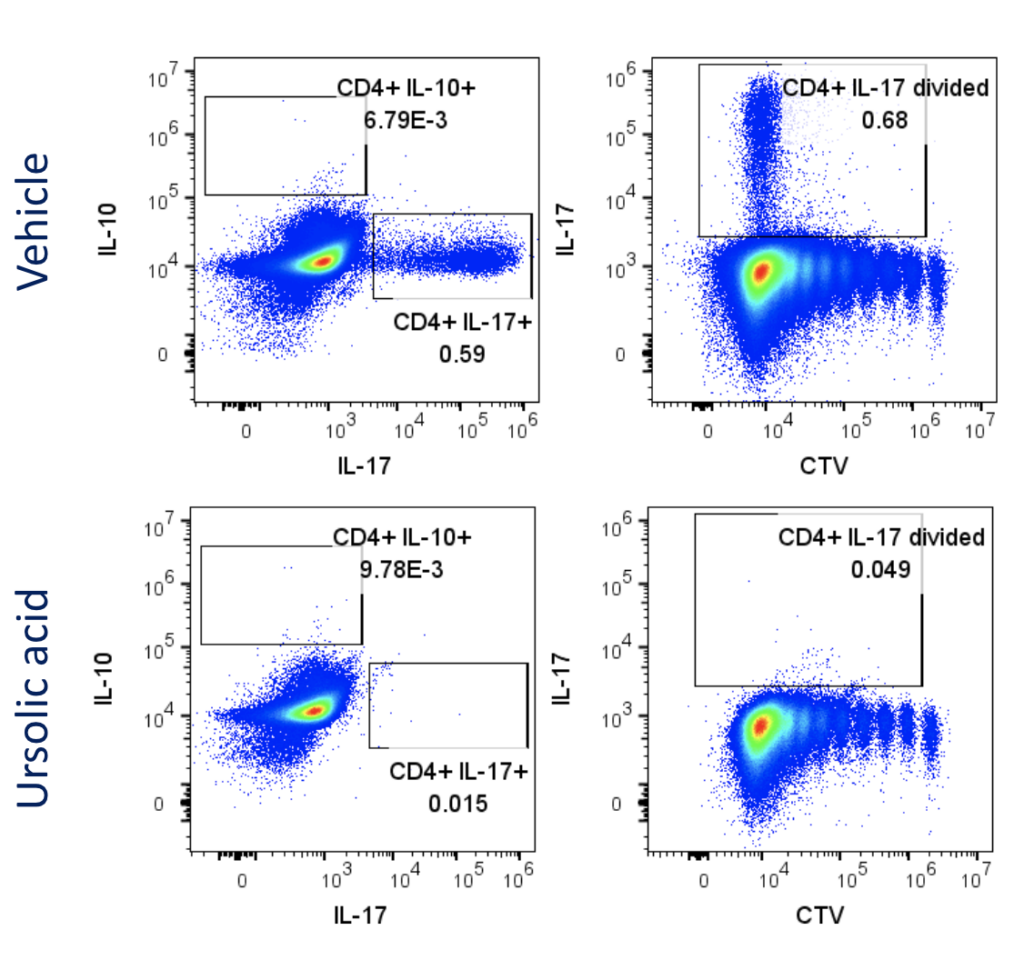
Evaluation of therapeutic modulation of Th17 differentiation
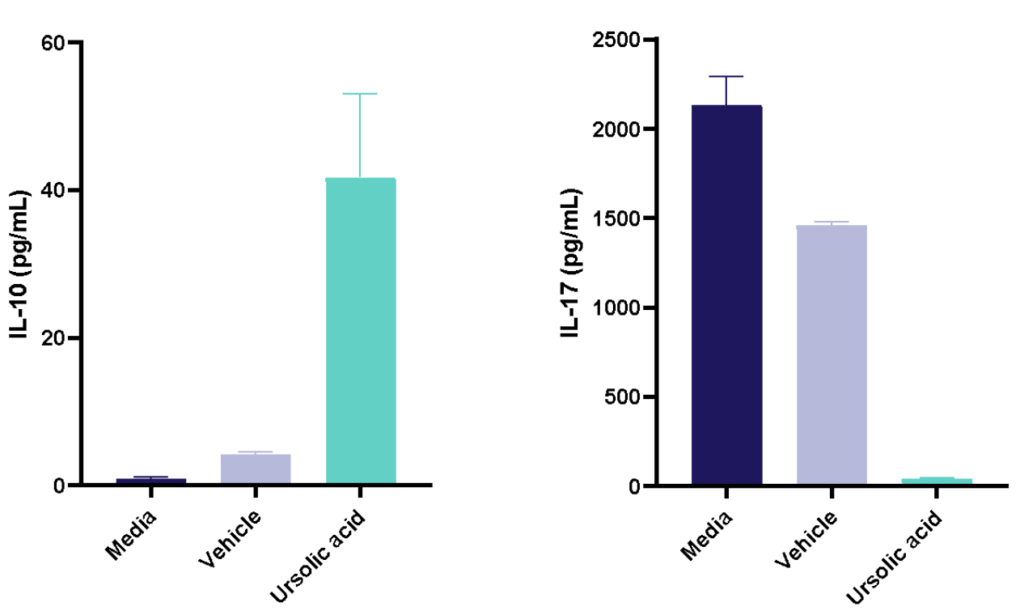
Figure 1: Polarisation of Th17 cells. Naïve CD4 cells were cultured under Th17 polarising conditions for 12 days in the presence or absence of Ursolic Acid. CD4 T cells were assessed for proliferation by CTV dilution; intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) of IL-17 and IL-10 by flow cytometry. On Day 12, Supernatants were collected and evaluated for IL-17 and IL-10 levels by MSD. RoRγT inhibitor Ursolic Acid showed selective inhibition of IL-17 production by intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) and MSD.
Evaluation of therapeutic modulation of Th17 effector function
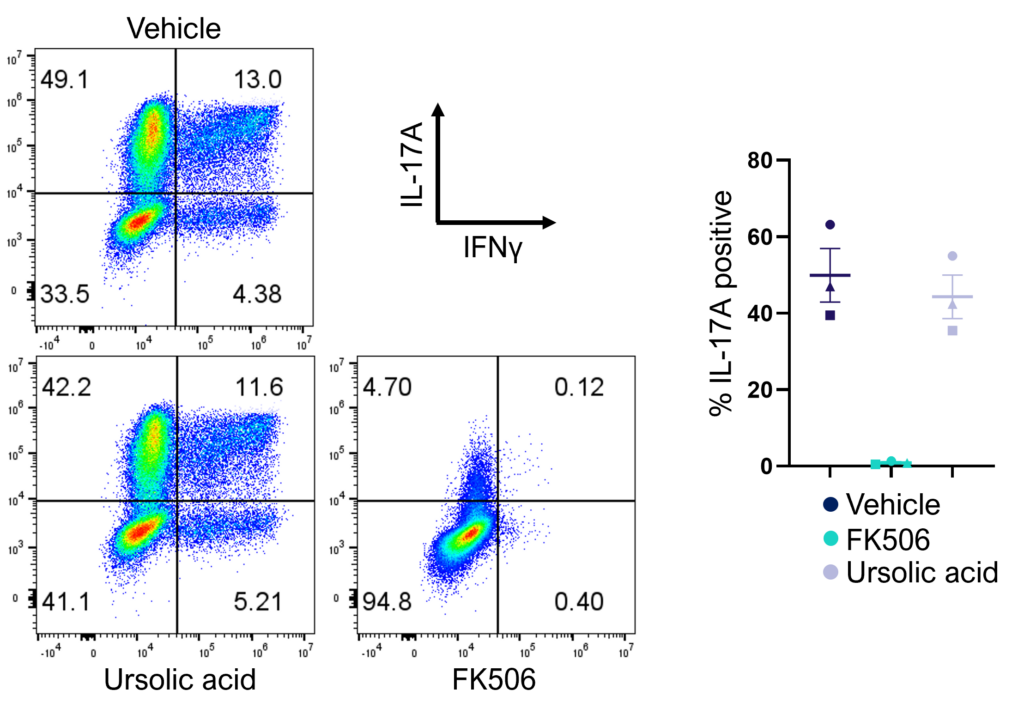
Figure 2: Inhibition of Th17 cell effector function. Magnetically sorted memory Th17 cells were polyclonally stimulated under Th17 conditions in the presence or absence of ursolic acid or FK506 for 5 days. A percentage of Th17 cells are polyfunctional (IL- 17A+IFNg+) and refractory to inhibition by ursolic acid (an inhibitor of Th17 differentiation) but not FK506.
Evaluation of therapeutic modulation of antigen-specific memory T cell responses to recall antigens
I. T cell response to Tetanus Toxoid, Influenza and PPD antigens
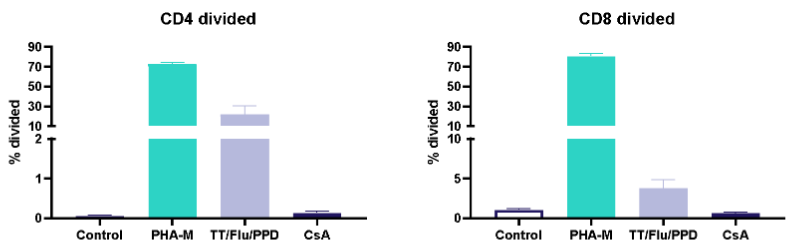
II. Dose response to Influenza antigen
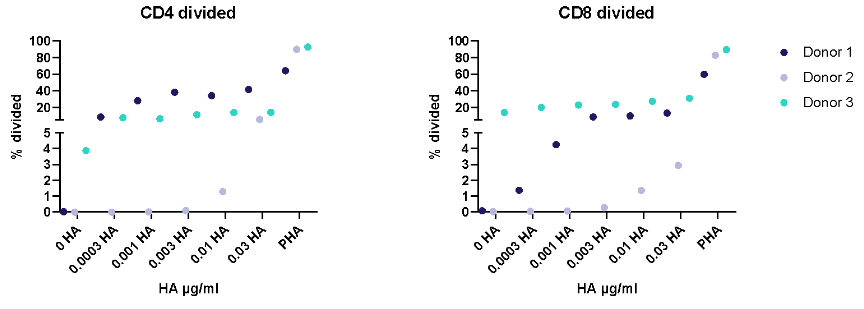
Antigen specific T cells response to a recall antigens. (I) Healthy donors PBMC were stimulated with PHA-M or triple antigen cocktail (Tetanus Toxoid, Influenza and PPD). Cyclosporin was used as a reference treatment. (II) Dose response to Influenza antigen. CD4 and CD8 T cells proliferation was measured by flow cytometry using CTV dilutions.
Enhance T cell effector function: benchmark novel therapies against immune checkpoint blocker (anti-PD-1) in a 1-way MLR

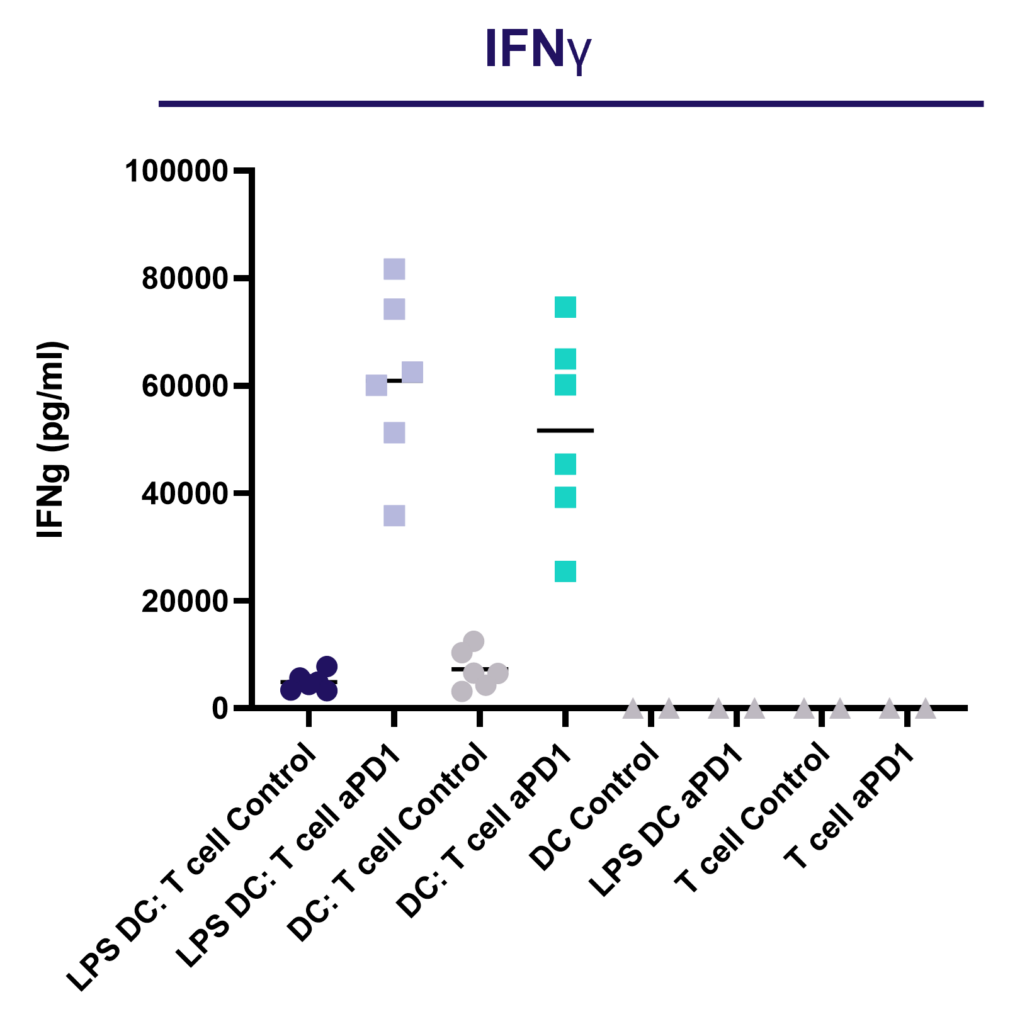
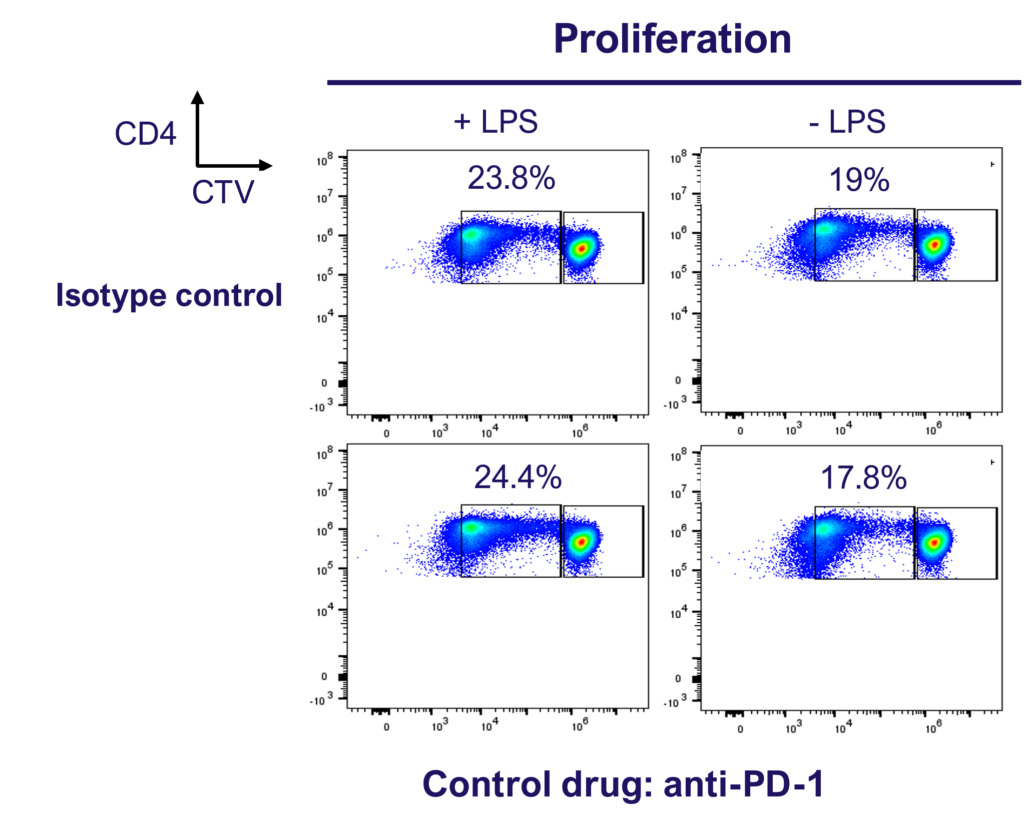
PD-1 blockade does not enhance CD4 T cell proliferation in a 1-way MLR as determined by dye dilution of CTV labelled CD4 T cell using flow cytometry.
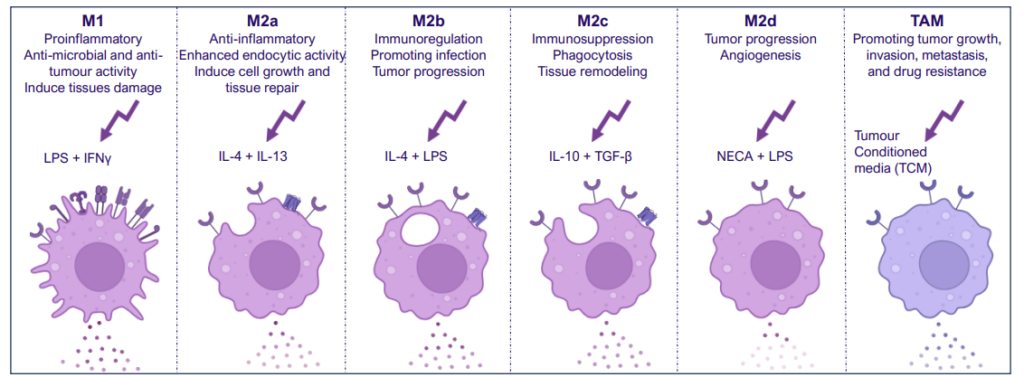
M1/ M2a-d polarisation assay
Monocyte derived macrophages (moMΦ) are differentiated from monocytes isolated from healthy blood donors followed by polarisation into a range of phenotypes M1/ M2a-d and TAM phenotypes using the stimuli described below. Readouts include flow cytometric analysis of surface markers associated with different subsets, production of cytokines and chemokines and ability to phagocytose. Therapeutics can be added at the monocyte to macrophage differentiation phase or polarisation phase to prevent or drive polarisation into a distinct macrophage phenotype.
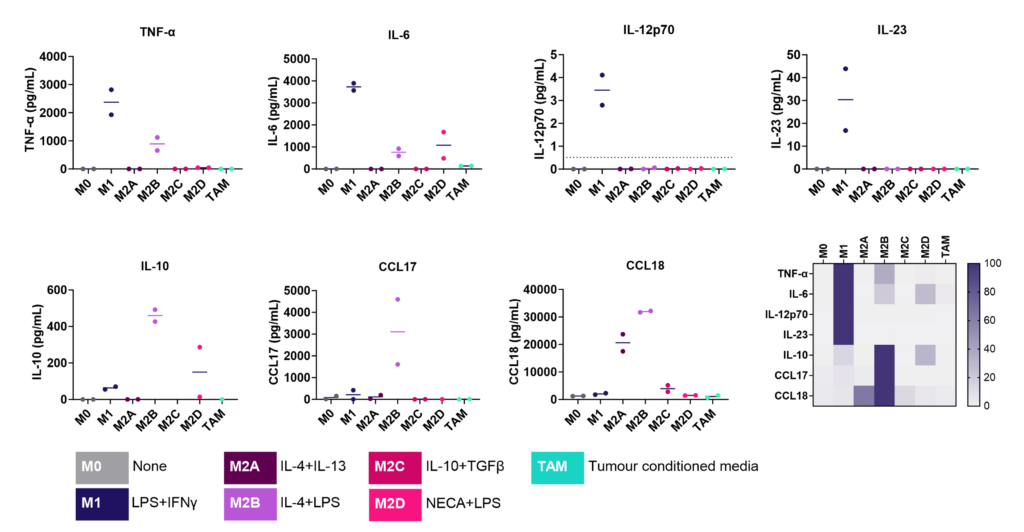
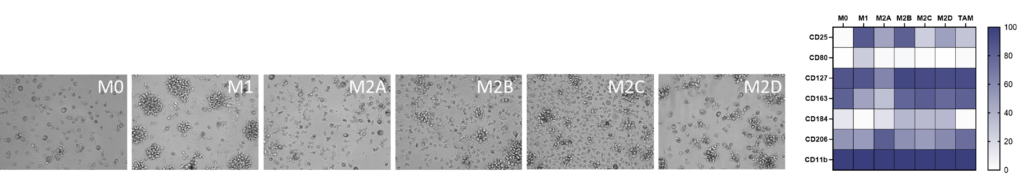
Screening assay to assess modulation of human M1/M2 macrophage function
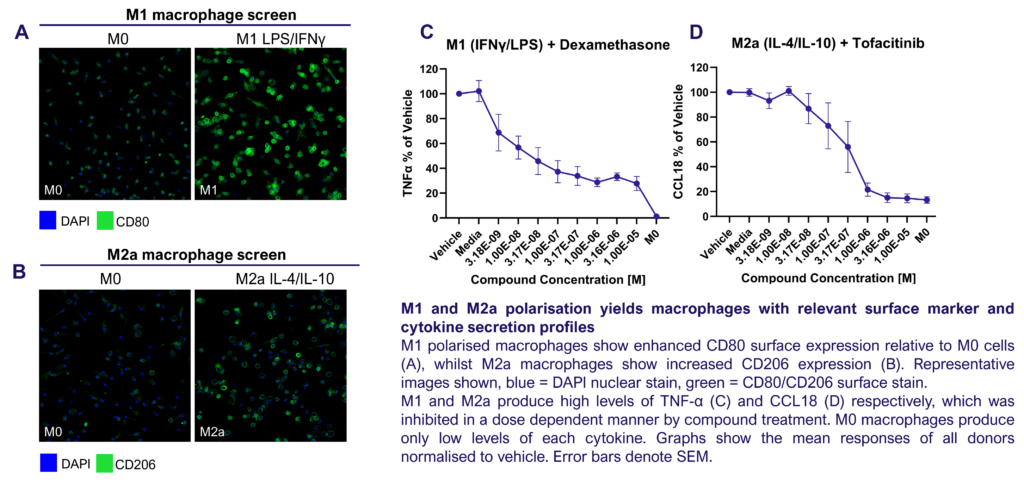
We present a medium-throughput human macrophage assay to screen novel therapeutics that modulate pro-inflammatory M1 (IFNγ/LPS) and anti-inflammatory M2 (IL-4/IL-10) macrophage subsets. Dexamethasone and tofacitinib are used as reference drugs for benchmarking.
Dysregulated macrophage polarisation exacerbates various diseases. Therapeutics that target macrophage re-polarisation could modify the disease state by shifting macrophages to a beneficial phenotype. For example, promoting an inflammatory M1 phenotype could benefit the tumor microenvironment, while fostering an anti-inflammatory phenotype could help in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
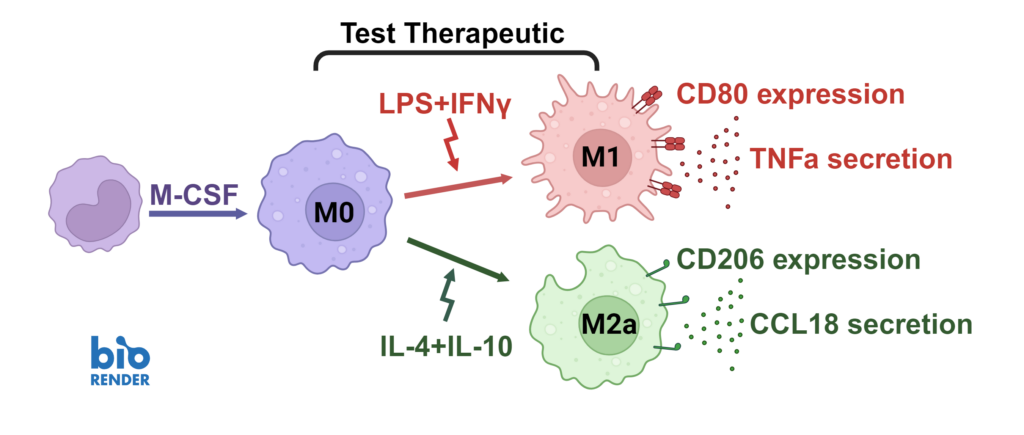
Macrophages were differentiated from monocytes and polarised to M1 or M2a phenotypes following the schema to the left. Polarisation was assessed through CD80 staining and TNFα secretion for M1, and CD206 staining and CCL18 secretion for M2a; staining quantified via HCS analysis. Inhibition of M1 and M2a polarisation was demonstrated using dexamethasone and tofacitinib as reference compounds. Novel therapeutics can be benchmarked against these references.
A THP-1 macrophage cytokine release assay (CRA) can be used to explore modulators of an inflammatory response or “de-risk” any potential unwanted effects of novel therapeutic delivery systems
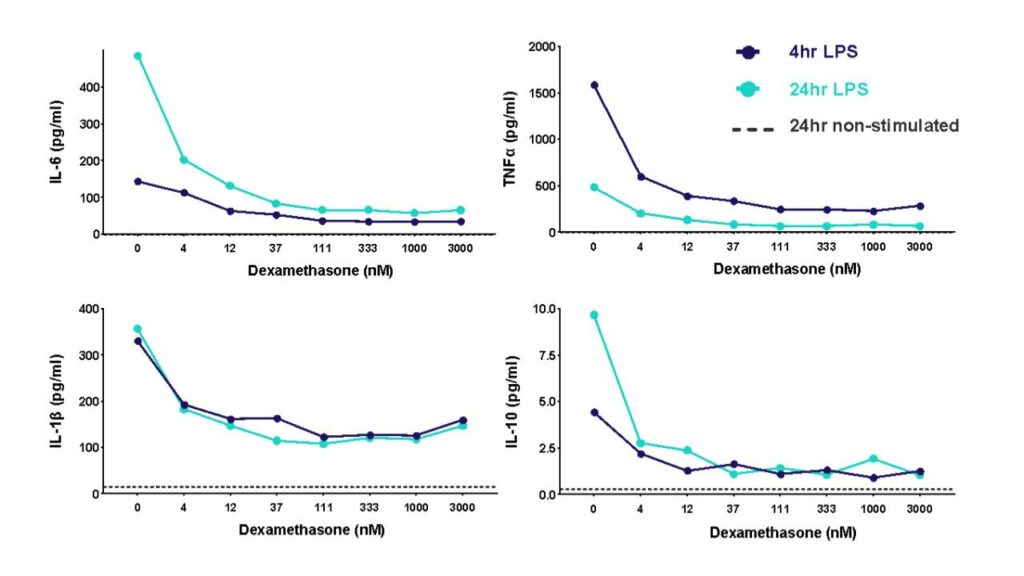
THP-1 cells were differentiated with PMA and then stimulated with LPS to induce cytokine release in the presence of different concentrations of the corticosteroid dexamethasone. Cytokine release was measured at 4h and 24h post LPS stimulation.
THP-1 macrophage cell line phagocytosis and efferocytosis
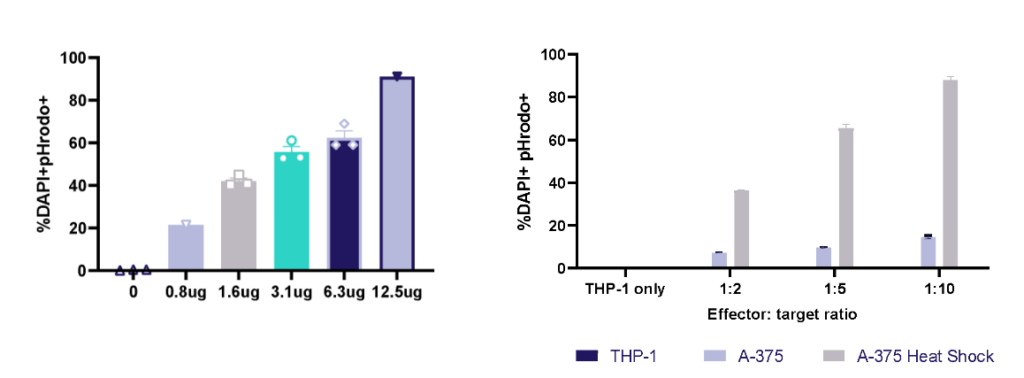
THP-1 macrophage phagocytosis of E.Coli bioparticles and efferocytosis of Heat Shock treated A-375 melanoma tumour cells. THP-1 cells were cultured with E.Coli bioparticles 0-12.5ug/ml; at 1h phagocytosis was evaluated by pHrodo+ cells using flow cytometry. THP-1 cells were cultured with three E:T ratios of A-375 or heat shock treated A-375; at 1h efferocytosis was evaluated by pHrodo+ cells using flow cytometry.
3D Tumour Killing Models: Tools for screening immune or tumour targeted therapeutics
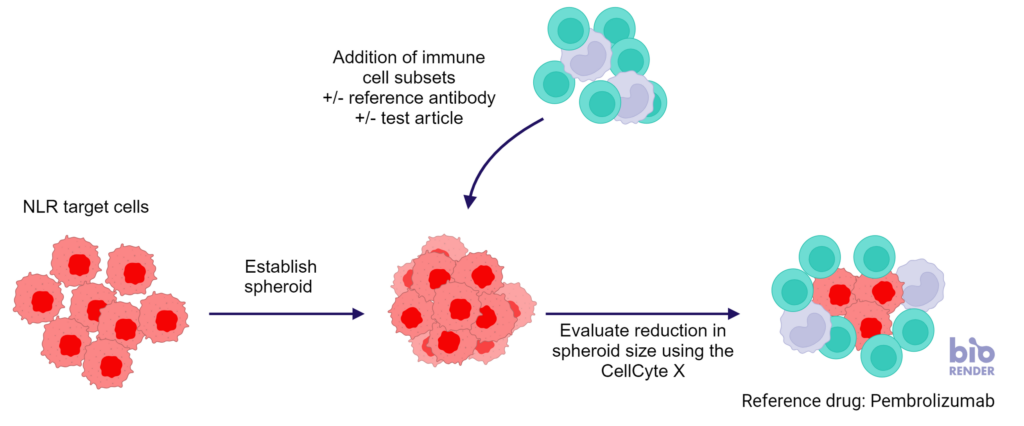
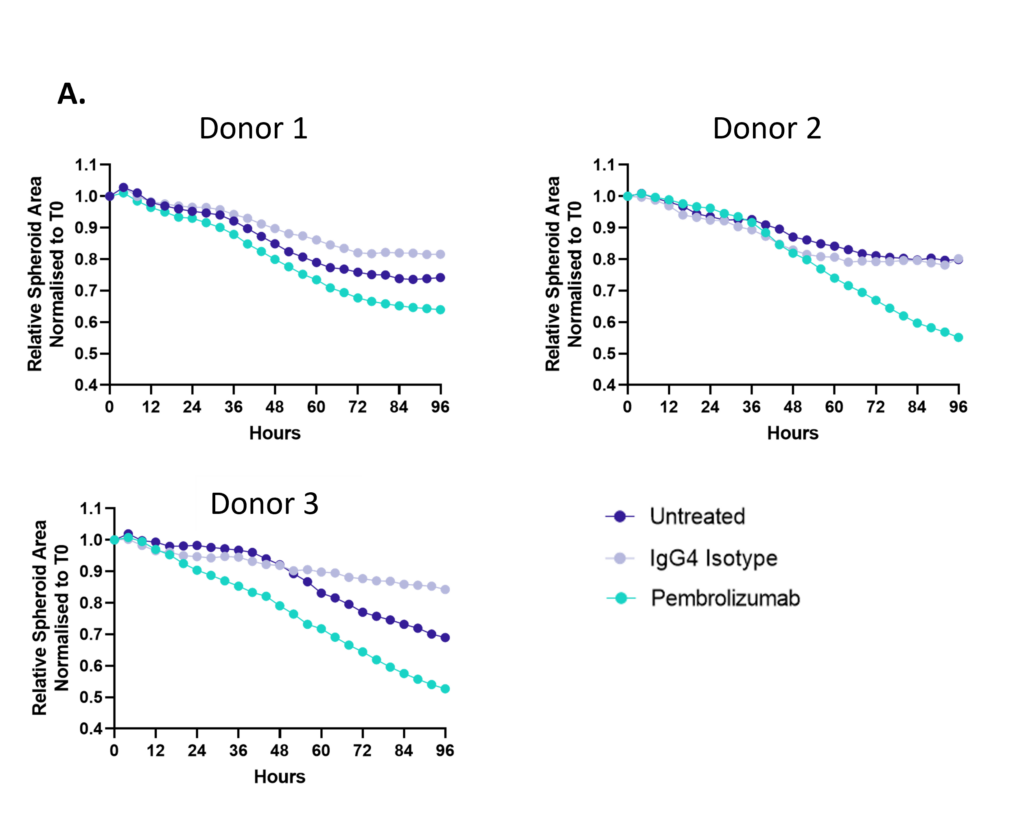
Figure 1: SKOV-3 NLR tumour cells were seeded into 96 well plates, PBMC were added once spheroids were established in the presence of Pembrolizumab or IgG4 control or vehicle (untreated) and imaged every 4 hours for 96 hours using the CellCyte X. Relative spheroid area (%) was measured (A). AUC statistics were calculated using GraphPad Prism v9.5.0
Enzyme-Linked Immuno Spot (ELISpot) is a technique which quantifies immune cells of low abundance which release biomarkers such as cytokines in response to antigenic stimulation. ELISpot is a highly sensitive method to test immune modulators, novel vaccine candidates or de-risk immunogenicity testing in an antigen-specific CD4 and/or CD8 T cell assay.
| Condition | Aim |
| No Stimulation | Negative control |
| PMA | Positive control |
| CERI (CMV, EBV, RSV, Influenza) | MHC-I restricted peptide pool to evaluate modulation of CD8+ T-cell memory response |
| CPI (CMV, Parainfluenza, Influenza) | Positive protein antigens to evaluate modulation of CD4+ T-cell memory response |
| CEF (CMV, EBV, Influenza) | MHC-I restricted peptide pool to evaluate modulation of CD8+ T-cell memory response |
| Cyclosporin A (CsA) | Inhibition of immune response |

Spot Forming Units (SPU) for IFN-γ per 100,000 PBMC from CERI, CPI and CEF antigens for three donors

Evaluation of therapeutic modulation of antigen-specific memory T cell responses to recall antigens
I. T cell response to Tetanus Toxoid, Influenza and PPD antigens

II. Dose response to Influenza antigen

Antigen specific T cells response to a recall antigens. (I) Healthy donors PBMC were stimulated with PHA-M or triple antigen cocktail (Tetanus Toxoid, Influenza and PPD). Cyclosporin was used as a reference treatment. (II) Dose response to Influenza antigen. CD4 and CD8 T cells proliferation was measured by flow cytometry using CTV dilutions.
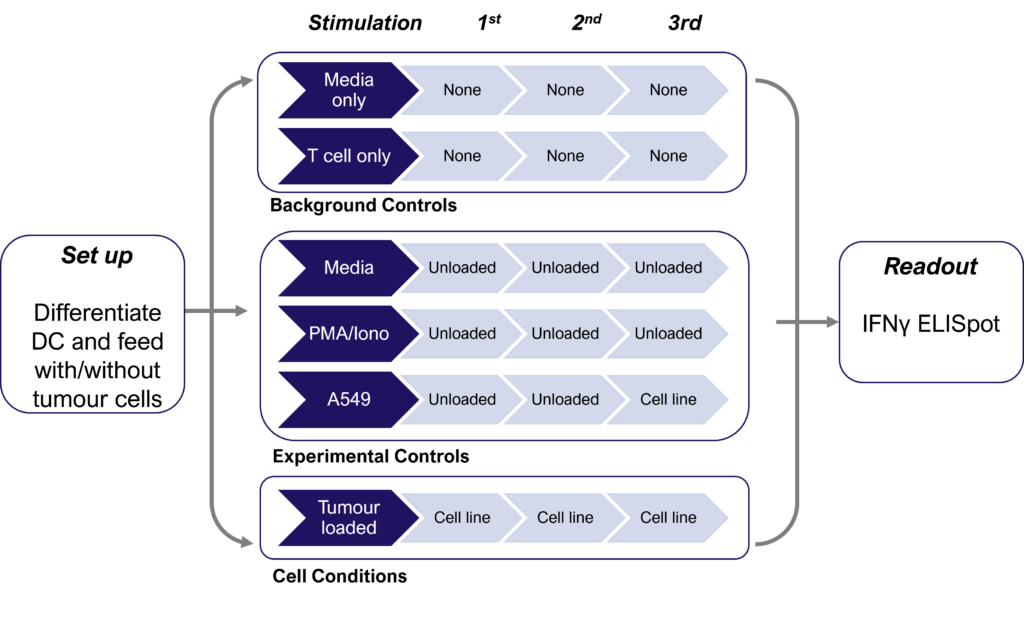
Dendritic cells fed with tumour cell lysates prime rare neoantigen-specific CD4 T cells and cross present antigen to prime neoantigen-specific naive CD8 T cells
Therapies targeting the modification of tumor cells to increase neoantigen expression and improve immune cell recognition are currently under development. Detecting these subtle changes typically involves several cycles of dendritic cell restimulation of T cells, followed by the sensitive measurement of rare neoantigen-specific T cell responses using IFNγ ELISPOT assays. The schematic below shows the assay design with multiple round of dendritic cell (DC) restimulation to expand rare neoantigen T cell responses.
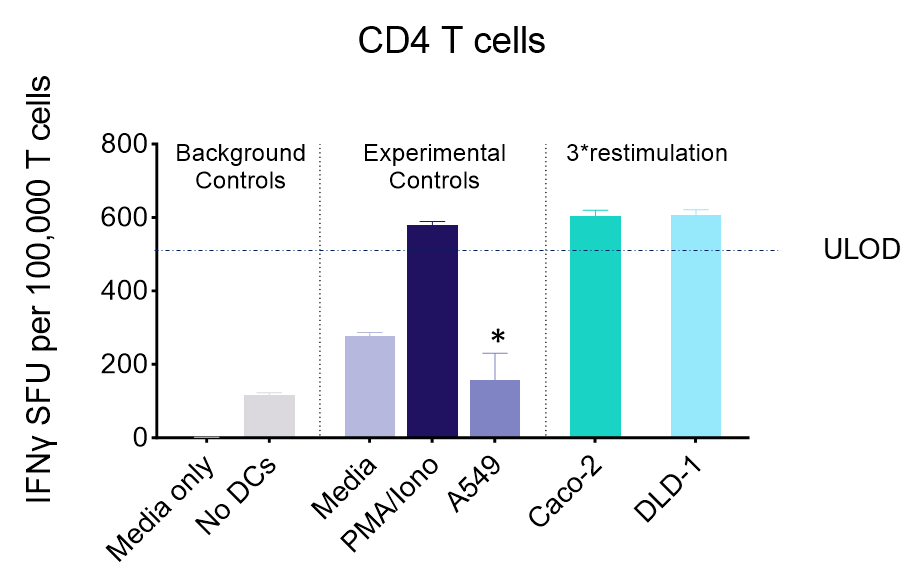
IFNγ release from activated tumour neoantigen-specific CD4 T cells
IFNγ release from activated tumour neoantigen-specific naive CD8 T cells
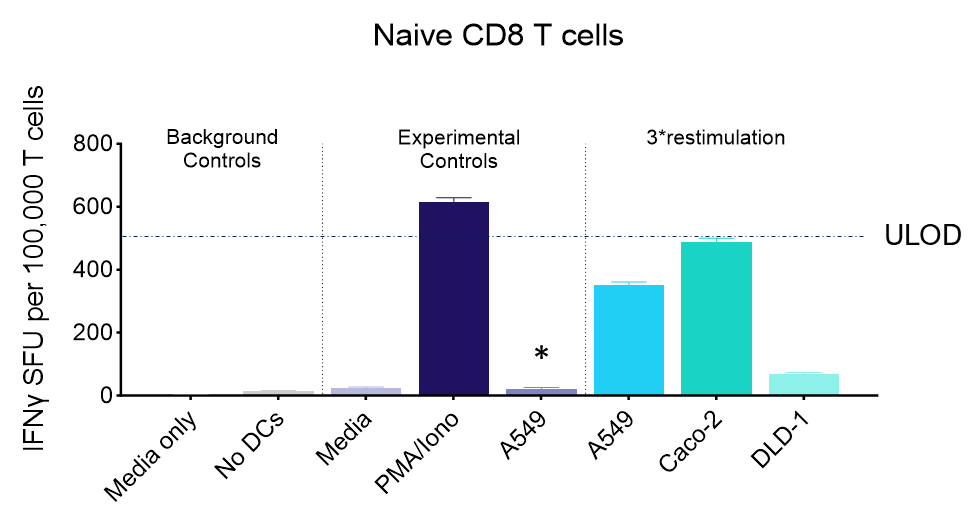
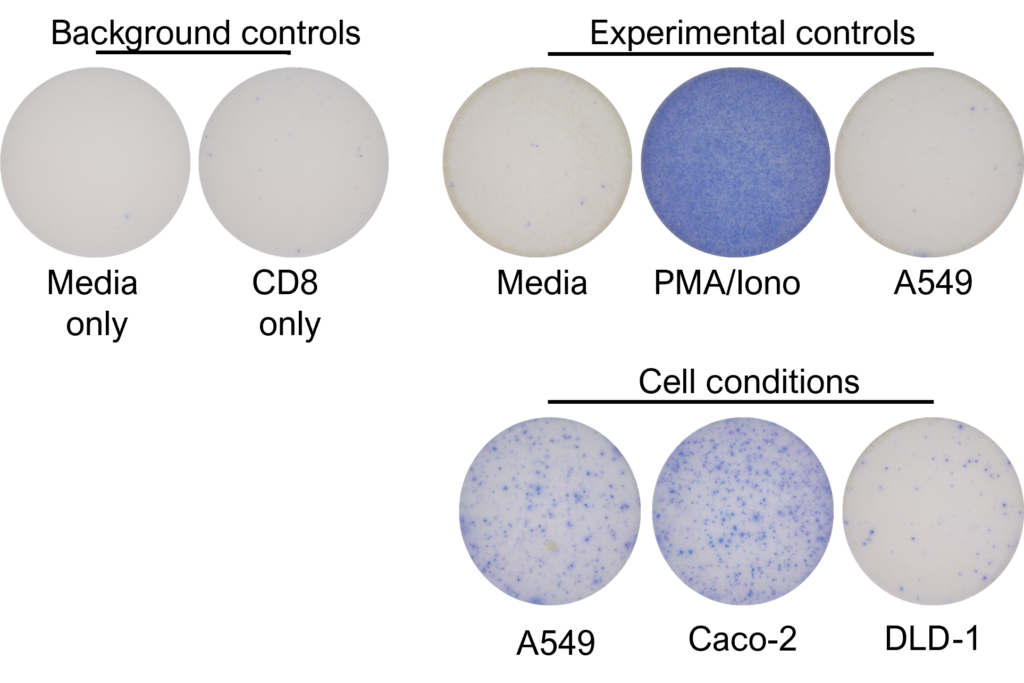
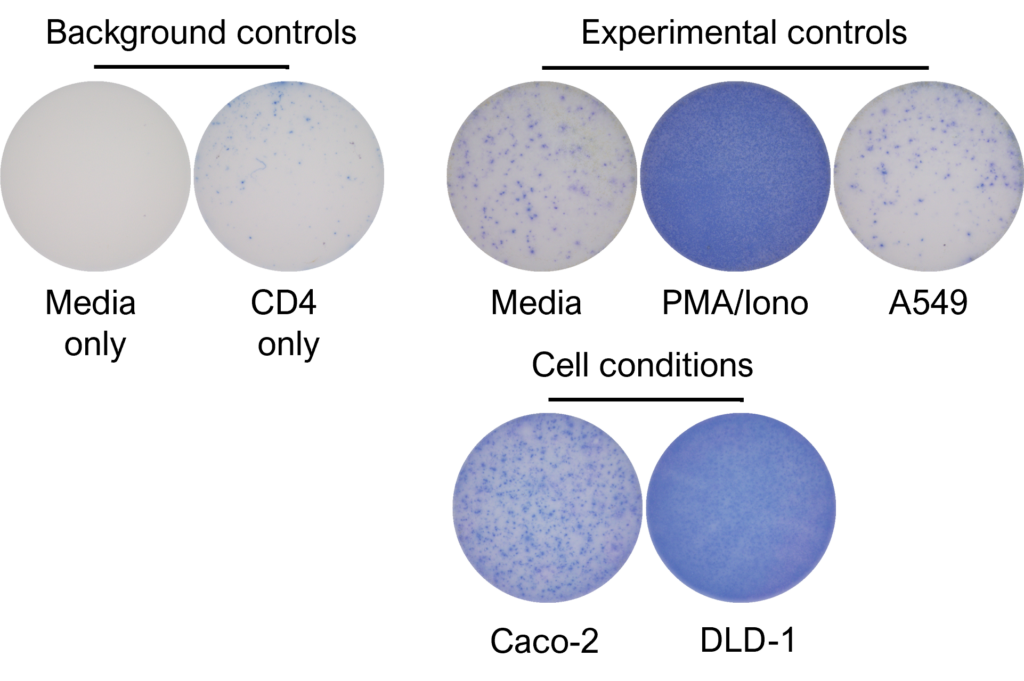
Figures: CD4 or naïve CD8 T cells were co-cultured with unloaded dendritic cells (DC), or with DC loaded with tumour cells that had been previously treated with media or vehicle. Three rounds of stimulation of T cells with DC were performed (* single round of DC stimulation). PMA and ionomycin were added as positive controls during the final round of stimulation. T cell stimulation was assessed by measuring the number of spot forming units (SFU) by IFNγ ELISpot. Media and T cell only wells were included as background controls. Number of SFU per 100,000 plated T cells, with mean of two (experimental controls) or three (all others) replicates ± SEM shown. Representative images of CD4 and naïve CD8 T cell IFNγELISpot. Each blue dot represents one IFNγ-producing T cell. ULOD = Upper Limit of Detection
3D Tumour Killing Models: Tools for screening immune or tumour targeted therapeutics


Figure 1: SKOV-3 NLR tumour cells were seeded into 96 well plates, PBMC were added once spheroids were established in the presence of Pembrolizumab or IgG4 control or vehicle (untreated) and imaged every 4 hours for 96 hours using the CellCyte X. Relative spheroid area (%) was measured (A). AUC statistics were calculated using GraphPad Prism v9.5.0
Antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) in a 3D tumour spheroid model

Figure 1: SK-OV-3 NLR cells expressing HER2 were plated were seeded into 96 well plates and once spheroids were established purified NK cells were added to cultures in the presence of Trastuzumab or IgG1 Isotype or IL-12/IL-15 or vehicle (untreated) and imaged every 4 hours for 96 hours using the CellCyte X. Relative spheroid area (%) was measured (A) and the AUC (B) calculated using GraphPad Prism v9.5.0. Line graphs show the mean of triplicate wells and the bar graph shows mean +/- SEM of 3 donors. (C) Representative images from the CellCyte X at 96 hours post NK cell addition to tumour spheroids.
